LPG Oil tanker LNG vehicles Thermal Imaging and Marine Inspections surveys
Infrared thermal imaging inspection service for oil tanker LPG/LNG ship
At present, the application of petroleum and LNG is changing with each passing day, offshore oil LPG and derivatives and LNG trade is also gradually expanding, and the number of ships using LNG as power around the world is also increasingPassenger ships, offshore ships, oil tankers, container ships and bulk carriers have begun to use LNG power propulsion, while conventional fossil fuel ships mainly have the risk of flammability and explosionThe main risk of the ship: In addition to the risk of flammability and explosiveness, there is also the risk of low temperature damage.

Refrigerated container ship container ship Oil tanker LNG vehicles
Thermal Imaging and Marine Inspections surveys
infrared thermography and ultrasonic testing
1. MSB thermal imaging service
2. ESB thermal imaging service
The mainstream oil tankers for crude oil transportation are VLCC (Very Large Crude Carrier) of 200,000-300,000 tons
VLCC/ULCC(very large crude oil carrier/ultra large crude oil carrier)
1. Suezmax tanker
Refers to the largest oil tanker that can pass through the Suez Canal at full load, i.e. with a draft of no more than 58 feet. The ship is designed to carry 100,000 tons of crude oil, and the deadweight is generally not more than 150,000 tons, so it is often called a "million barrel oil tanker".
2. Aframax tanker
Refers to oil tankers with a deadweight of 8-100,000 tons. With a design draft of 12.20 meters and a design capacity of no more than 80,000 dwt, the vessel can call at most North American ports and can achieve the best economy. The maximum load capacity of this type of ship is obtained by adjusting the structural draft. It is generally referred to as a "freight ship" or a "U.S. tanker".
3. VLCC/ULCC (very large crude oil carrier/ultra large crude oil carrier).
Refers to jumbo oil tankers and very large oil tankers. VLCC first appeared in 1967, and the deadweight tonnage is generally less than 300,000 tons; The carrying capacity of ULCC is more than 300,000 tons, and it appeared in 1969. The two types of tankers are the result of the war in the Middle East that has led to a significant increase in the distance of oil transportation from the Persian Gulf to Europe and North America. At present, VLCCs are more used on the Middle East-Far East route, while ULCCs are mostly used for offshore oil storage vessels.
4. Shuttle tanker
Refers to a type of oil tanker specially used for transporting oil from offshore oil fields to land. Due to the high technical requirements for offshore oil transfer, most of these ships are equipped with a series of complex loading and unloading systems, and most of the ships are equipped with dynamic positioning systems and helicopter platform facilities, and the cost is much higher than that of oil tankers of the same tonnage. At present, the carrying capacity of shuttle cruise ships is mostly between 8-150,000 tons.
Structural features of oil tankers
The main component of the tanker structure is the design of the hull or external structure. A tanker with only one hull between the hull and the ocean is called a single-hull tanker. Most tankers are double-hulled, with an extra space between the hull and the tank. Double-bottom and double-sided, etc. The hybrid design combines aspects of both monocoque and bicoque designs. In accordance with the amendment to Annex I of the MARPOL Convention, all single-hull tankers have been phased out since 2015.
1. Characteristics of oil tanker fires
There are many oil and water pipelines in the oil tanks of oil carriers (also known as oil tankers), and different pipelines are generally interconnected
intertwined. In the event of a fire on an oil tanker, not only the smoke in the cabin is large, the visibility is low, the temperature is high, and toxic gases are produced
It is difficult for personnel to escape, and the speed of combustion and explosion is very fast, and the fire will penetrate up and down, develop vertically and horizontally, and form
Three-dimensional fires often cause ship destruction and death.
Secondly, the heat conduction of the hull steel of the oil tanker is also relatively fast, and the radiant heat is strong, which can cause the adjacent oil tanks after the fire
The oil is heated and vaporized, and a continuous explosion occurs. When an oil carrier explodes, it will not only cause the oil to overflow to the water.
Large-scale burning of the water surface will be formed, and it will also bring serious pollution to the water.
According to the analysis of past accidents, there was a fire and explosion on an oil tanker, and there were more empty tanks than full tanks, and more crude oil than gasoline. This is
Because when the tanker is sailing in empty tanks or ballast (water storage), the stability performance of the ship is poor, and it is not as stable as when carrying oil. Empty tanks, or so-called "ballast" tanks filled with some water, are not really "empty" because there is some residual oil and a lot of oil and gas in the cabin
When these oil and gas are mixed with air in a fixed ratio, they can form an explosive mixture, which will occur when encountering an open flame
Powerful explosions.
Other than that. During the combustion process of ships transporting heavy oil products, the flame will also rise and fall. This is because
The fraction of heavy oil and light oil is different, and when the light components on the surface of heavy oil are rapidly evaporated and burned, the flame appears to "rise".
When the light components of the surface layer of heavy oil are burned off. The light ingredients in the lower layer have not yet had time to evaporate
Entering the "volt" state can easily make the rescuers misjudge. If the oil tank is filled with heavy oil with more moisture, when there is an explosion and combustion, sometimes there will be boiling or splashing of heavy oil, which will cause the fire to expand and spread, threatening personal safety.
The causes of oil tanker fires are generally concentrated in reef collision, collision, capsizing, use of open flames, electromechanical short circuit, static electricity, welding, etc
Several aspects.
Preventive measures against fire on tankers/LNG carriers
The first is the combustible monitoring of the mixture of combustible gas and air in the ship, in the combustible gas mixture on board, the ratio of combustible gas to air (or oxygen) can only occur within a certain range. Above or below this range will not burn. In general, the minimum volume concentration at which a combustible gas can burn in its mixture with air at 1 atmosphere is called the lower limit of combustion (LFL), and the maximum concentration of volume is called the upper limit of combustion (UFL). The concentration between the upper and lower limits is called the combustion range of combustibles (usually between 1% for LFL ~ 10% for UFL). It must be noted that there may be thousands of potential ignition sources, and the prevention and control of ignition sources is always an extremely important part of fire and explosion prevention.
Open flames must be prohibited on the deck of an oil tanker/LNG ship and any other premises where there may be an oil/LNG hazardand welding.
Over-temperature monitoring and over-current/leakage current monitoring and short-circuit protection for electromechanical equipment and facilities
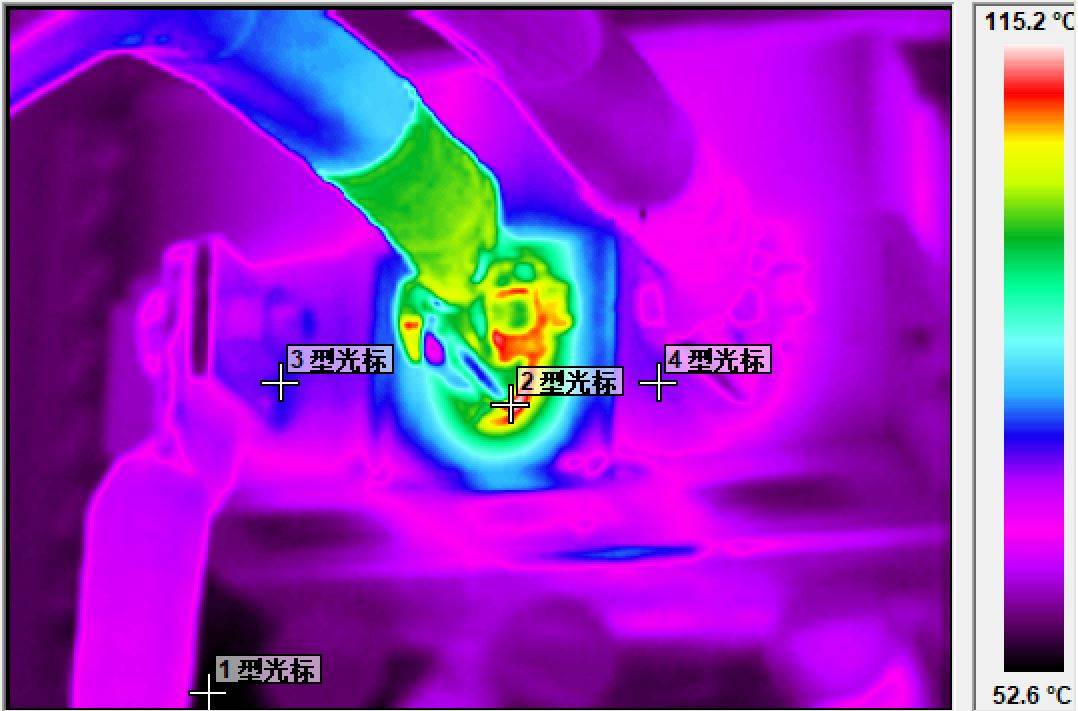
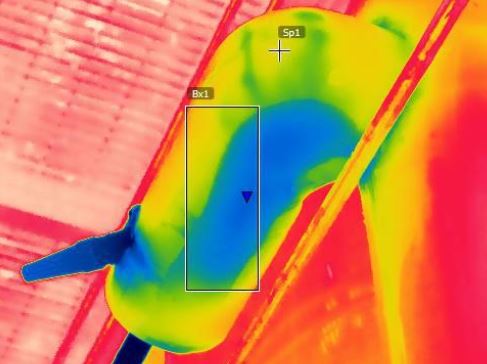
(1) Install NKTEVA6 distribution red array detectors in key equipment for real-time monitoring, and capture thermal images or videos of the parts of the electrical equipment and lines that are heated;
(2) Conduct a comprehensive heat scan of all electrical equipment and lines every year or cycle, and make temperature records, find abnormal heating parts, capture records, and make thermal imaging reports.
(3) Analyze the causes of heating of electrical equipment through thermal imaging diagrams, and carry out corresponding maintenance, fastening or replacement of components, etc.;
In addition, the NKTEVA6 distribution red array detector can also detect leaks in pipelines, tanks, LPG or LNG on oil tanks. Usually LPG LPG pipeline tanks are stored at a temperature of -20°C for 10 bar and LNG for 1 bar on tankers The temperature is -162°C, which is generally lower than the ambient temperature at room temperature, so the storage of LPG or LNG can be observed by the NKTEVA6 distribution red array detectorThere is a significant leak in the pipe tank.
At present, new and renovated LNG power vehicles ships are equipped with temperature, pressure, liquid level, and gas concentration sensors, combined with combustible gas detectors, etc., to monitor the leakage of LNG supply systems, such as full-capacity LNG storage tanks, in LNG The top and outer wall of the tank are equipped with a combustible gas detector and a flame ion detector to monitor the natural gas generated after the LNG leakage and the flame ions generated by the combustion of natural gas, and 8 thermocouples are installed on the tank wall and the bottom of the tank, and whether there is a leak according to the temperature measured by the thermocouples, but due to the limitation of the number of thermocouples, The temperature detection range is small, and the leakage of LNG pipelines and tanks can be quickly detected by increasing the NKTEVA6 distribution, temperature visualization and large radiance of the red array detector. LNG is ultra-low temperature, and its leakage will vaporize quickly. The NKTEVA6 Distribution Red Array Detector is a rapid detector of temperature, which can effectively capture the location of the leak according to the leak point and the change in the ambient temperature. Non-contact temperature measurement with the NKTEVA6 Red Array detector also enables the detection of fires and ignition sources in the vicinity of the LNG tank system. The NKTEVA6 distributed red array detector can be installed in a fixed online or modified into a handheld one as a mobile inspection and maintenance tool.

